Global
International


Fibre preparation, yarn-spinning, twisting, winding and finishing are demanding processes that require high-quality Tangential Belts.
We offer a complete range of RAPPLON® High Performance Flat Belts for the Textile Industry. These products satisfy the ever increasing needs and provide extended service life as well as improved chemical and aging resistance.
Explore using the drop-down menu or by clicking on the pointers
This infographic is used as a general indicative example only.
Actual factory and process configurations could vary, but our industry experts know them all.

In the spinning mill, the bale opener is the first link in a long chain of processing steps in producing yarn. The bale opener releases fibre lumps out of the bales and transfers the fibres by airflow into the cleaning section.

Carding machines align lose fibres into tufts or fleece. Carding machines are driven by power transmission belts and have sliver tapes installed to guarantee a frictionless output of the carded sliver out of the machine.

The draw frame stretches and parallelizes the textile fibres, a process that balances inequalities within the slivers. The card slivers pass through several stretching units between weight-loaded rollers and are spun down in loops into spin cans.

Combing is a process to prepare fibres for spinning and produces smoother, finer, stronger and more uniform yarns. Combing is commonly confined to high grade, long staple natural fibres.

The spinning machines stake the roving, thin it and twist it, creating yarn. The roving is pulled off a bobbin and fed through rollers, which are feeding at several different speeds. This thins the roving at a consistent rate.

The rotor spinning process is much more efficient than Ring spinning and is mainly used for coarse yarns.
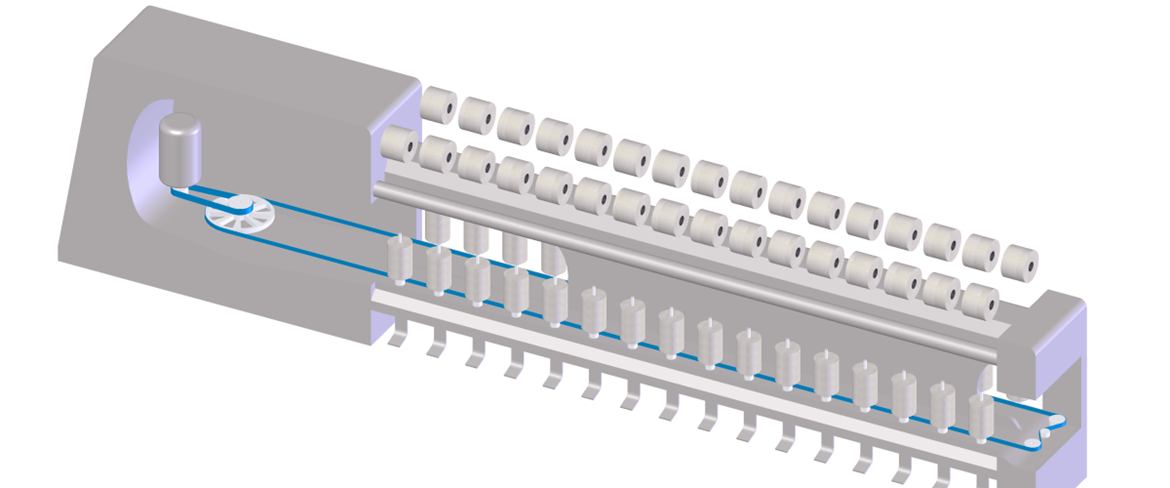
Two or more single-end threads are twisted together to form one multi-ply twisted yarn. Spindles are driven by tangential belts or by separate motors.

Winders are machines for wrapping string, twine, cord, thread, yarn, rope, wire, ribbon, tape onto a bobbin. Modern machines are equipped with Elastic Belts for transporting the cop while older machines are driven by Tangential Belts.
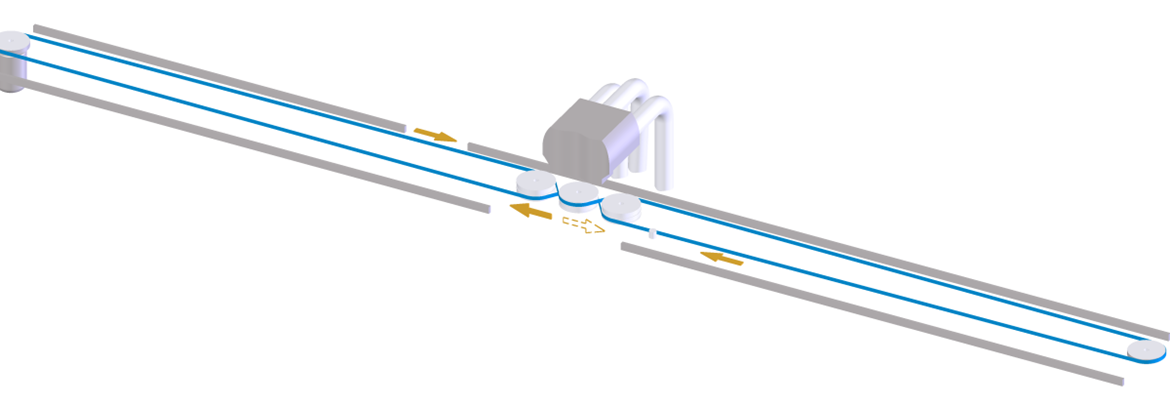
For cleaning Open end, Ring-spinning, Twister, Winder and Flyer machines pneumatically. Travel cleaners dramatically minimise manual cleaning work. Flat belts move the machine forward and backward and drive also the vacuum cleaner.

Man-made fibres are in general very even and have less “character” when it comes to the sense of touch. Texturing is the formation of crimps, loops, coils or crinkles in filaments to give the yarn typical characteristics.
| Article Code | Description | Force at 1% elongation dynamic | Info | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIN en ISO 21181 | Thickness | Minimum pulley diameter | |||
| dynamic | flexing | ||||
| FBGG054734 | GG S06.18 RFC | 6 N/mm | 1.8 mm | 40 mm | |
| FBGG054370 | GG S09.22 RRC green | 9 N/mm | 2.2 mm | 60 mm | |
| FBGG054528 | GG S11.25 RRC green | 11 N/mm | 2.5 mm | 60 mm | |
| FBUU054551 | UU N16 SSQ FG | 1.1 mm | 20 mm | ||
*Recommended Products are some examples of our solutions in a specific process. Consult your local Ammeraal Beltech expert to determine the most appropriate belt type, colour and material combination for your specific requirements and local stock availability.
By continuing to browse our website you agree to our use of cookies and Privacy Policy. More information about cookies.